What Is a Laser? How Does It Work?
Last Updated on
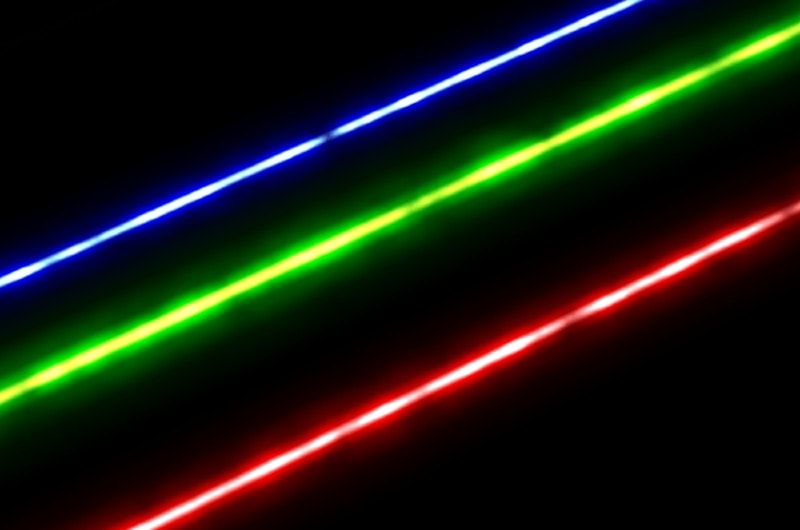

A laser is a highly concentrated light beam. It is generated by a device that amplifies light waves. The word “laser” is an acronym for “light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation.”
Lasers have many uses, including cutting and welding materials, measuring distance, and treating medical conditions. Laser beams can be very intense, so they must be used under supervision.
Here’s an overview of how lasers work and why we use them in different industries.

How Does It Work?
The working principle of a laser is based on the excitation of electrons. Electrons are particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. They become excited and jump to a higher energy level when they absorb energy.
It can happen when they are heated or when they absorb light photons. When electrons fall back to a lower energy level, they release the excess energy in the form of photons. A laser beam occurs when these photons are emitted in a parallel, coherent, and amplified manner.
Coherent light is light with waves that are in phase with each other. It means that the crests and troughs of the waves line up. Therefore, laser light is different from regular light.
It has the following distinguishing properties:
Monochromatic
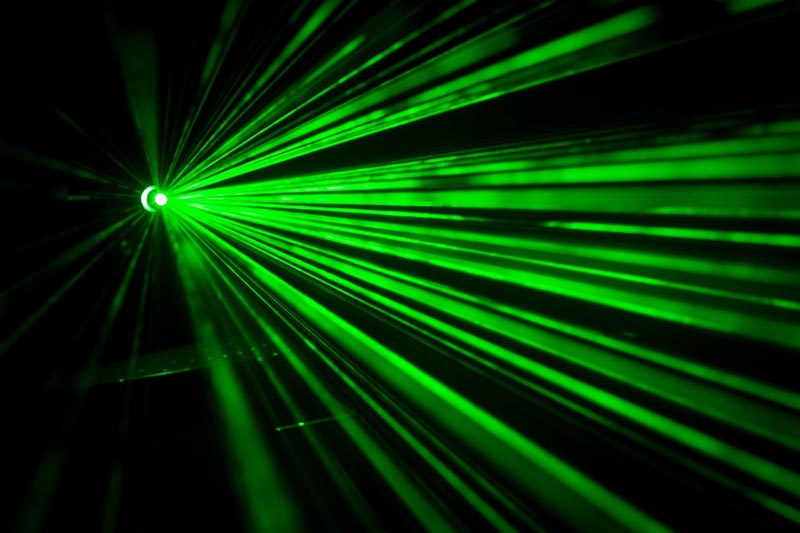

Laser light has a single specific wavelength. Therefore, it is different from regular light, which is a mixture of different wavelengths. The light wavelength a laser has will depend on the energy electrons release when they come to a lower orbit.
Directional
A laser beam is concentrated in a single direction. Thus, it does not scatter the way regular light does.
Coherent
The wavefronts of all photons in laser light move in unison. Simply put, all the photons are in phase with each other. This means that the light waves from different parts of the beam will reinforce each other instead of canceling each other out.

What Are the Different Types of Lasers?
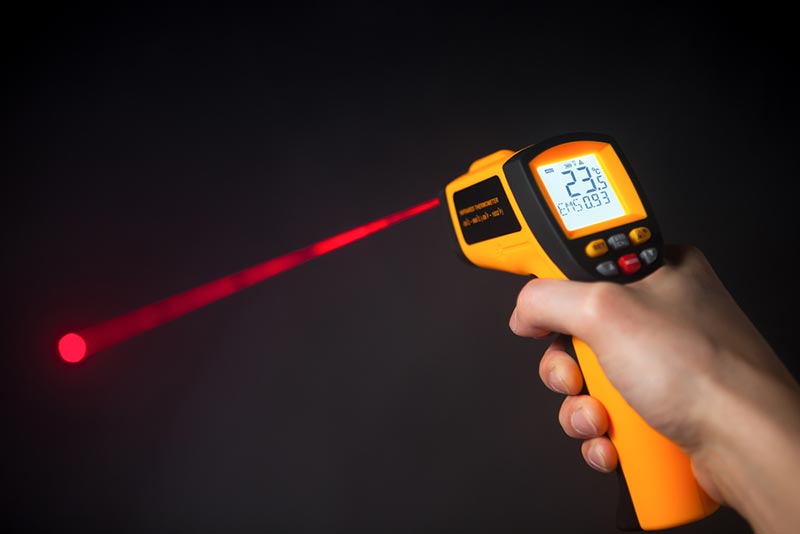

Lasers are categorized based on their wavelength, coherence, and power. There are five main types of lasers.
They are helpful in many industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and communications. Nowadays, there are new applications for these lasers too. A good example is laser holography.
Here’s a detailed look at the five types of lasers:
Gas Laser
In a gas laser, an electric current passes through a gas to create a plasma amplifying light. Standard gas lasers include carbon dioxide lasers and argon-ion lasers.
The most common gas lasers are carbon dioxide lasers. They are used in the industry for cutting and welding. They can also be used for medical purposes, such as surgery.
The principle of gas lasers is based on population inversion. In this process, electrons in an atom first move to a higher energy state. Then, they are quickly brought back down to the lower energy state, emitting a photon.
The photon then stimulates other atoms to emit photons. It results in a population of inversion and amplification of light.
- Air pollution measurement
- Barcode scanning
- Spectroscopy
- Holography
- Laser surgery
- Material processing
Solid-State Laser
A solid-state laser uses solid-state gain media instead of liquid, gaseous, or other gain media. The term “solid-state” refers to the gain medium, whereas “solid-state laser” is a laser in which the active medium is a solid.
- Neodymium
- Chromium
- Erbium
- Ytterbium
- Thulium
- Nd: YAG laser
- Er: YAG laser
- Ho: YAG laser
- Tm: YAG laser
Solid-state lasers are common in LIDAR technology. In LIDAR, a solid-state laser creates a beam of light reflected off objects in the environment. A detector captures the reflected light. Then, it uses light to create a 3D map of the region.
Solid-state lasers also help in medical applications, such as removing kidney stones. Plus, they help with tattoo removal.
Semiconductor Laser
A laser diode or an injection laser is a semiconductor device that emits coherent light. During operation, the device is pumped with electrical current or light from another laser.
It is used in various applications, including fiber-optic communications, barcode scanners, and laser pointers.
Liquid Laser
A liquid laser has an organic dye that works as a gain medium. Therefore, it is also known as a dye laser. The liquid can be pumped with another light source or an electrical discharge.
- Laser printers
- Spectroscopy
- Holography
- Medical diagnosis and treatment
Since liquid lasers are tunable, the user can control the light wavelength. So, it’s possible to produce different colors using the dye laser.
Fiber Laser
- Erbium
- Ytterbium
- Neodymium
- Dysprosium
- Thulium
- Praseodymium
Compared to other lasers, the laser beam is smaller and straighter in fiber lasers. As a result, they are more precise.
- Low maintenance
- Small footprint
- Low operating costs
- High electrical efficiency
Due to these properties, fiber lasers have many applications. For instance, they are useful in laser cleaning, welding, marking, and cutting.
Others
Besides properties, lasers can also be grouped based on their operation. There are two main operational types of lasers: continuous-wave and pulsed.
A continuous-wave laser emits a constant beam of light, usually visible to the naked eye. These lasers are helpful in welding and cutting.
Meanwhile, a pulsed laser emits light in short, intense bursts. Pulsed lasers are common in medical treatments and scientific research.
Pulse lasers tend to be more powerful due to the intervals. Energy builds during these intervals, allowing the pulse laser to produce powerful peak pulses.

Where Is It Used?

Lasers have a wide range of applications. They are used in multiple industries, such as medical, military, commercial, and scientific research. Here are some notable uses of lasers.
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is the process of using a laser to cut materials. Lasers can cut through several materials, including metal, plastic, glass, and wood.
That’s why they are common in manufacturing and construction. Laser cutting is a precise process that results in little to no waste.
Laser Engraving
A laser also allows for engraving. It is the process of using a laser to etch an image or message onto a surface.
For example, you might see laser engraving on jewelry, awards, or tools. Laser engraving works on many materials, such as metal, glass, wood, and leather.
Laser Printing
Laser printers are a common occurrence in most offices and homes. They use a laser to print documents, photos, and other images.
Laser printers are quick and produce high-quality results. In a laser printer, the laser beam “draws” the image of each page on a rotating drum coated with a photoconductive material.
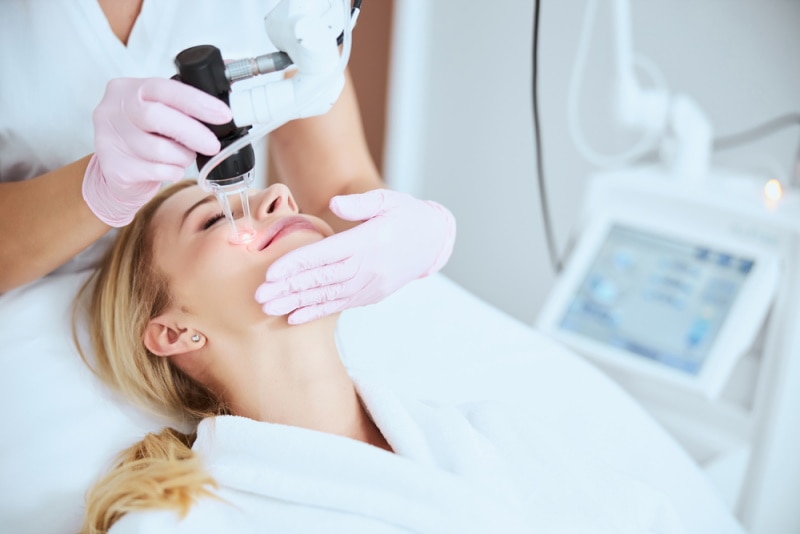
Laser Surgery
Lasers are also used in surgery for cosmetic procedures and more serious operations. Laser surgery is precise and can result in less bleeding and scarring.
Some examples of laser surgery include LASIK (laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis), used to correct vision, and laser skin resurfacing for treating wrinkles and other blemishes.
Photolithography
Photo means “light,” and lithography comes from the Greek words for “stone” and “writing.” So, photolithography is literally “writing with a light on stone.”
In the semiconductor industry, photolithography is the process of using light for etching circuitry onto silicon wafers. The circuit-etching is a critical step in the manufacturing of computer chips.
The light used in photolithography is focused through a lens onto a wafer. The light beam draws the desired pattern on the wafer, which is then transferred onto the silicon.
Laser Pointers
Laser pointers are handheld lasers emitting a thin light beam. They are commonly used in presentations to point at objects on a screen or wall.
Laser pointers usually emit visible light, but some emit infrared or ultraviolet light. Infrared and ultraviolet laser pointers are not safe for human eyes, so they should be used with caution.
While laser pointers are primarily used for presentations, they have also become popular toys for pets and children.
Laser Cladding
In laser cladding, a laser coats a substrate with a material layer. The process helps repair or protect surfaces from wear and corrosion. Laser cladding works on various materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics.

Advantages of Lasers

Lasers have many advantages over traditional light sources. Here are some of them.
Directional
Lasers are highly directional, emitting light in a very narrow beam. It makes them ideal for applications requiring precise targeting, such as surgery, scanning, and measuring.
Intense
Laser beams are powerful enough to cut through metal and other materials. They can also be used to weld and engrave.
High Accuracy
Since laser beams are precise, they are helpful in 3D printing and other applications requiring high accuracy. In addition, the accuracy allows for less waste and less material usage.
Modulation Capability
Modulation means the laser beam can be turned on and off quickly. It allows for quick encoding of information into the light.
The modulation capability of lasers allows them to be used for information storage and retrieval, such as in CD and DVD players. It also makes lasers suitable for communication purposes.
Environmentally Friendly
Lasers are becoming increasingly popular because they are more environmentally friendly than traditional light sources. In addition, they don’t produce harmful chemicals or pollutants.
Simple Design
Most lasers have a single light source and don’t require complex optics. That makes them relatively easy to design and build. Plus, most of them are economical.
Disadvantages of Lasers
Although lasers have many uses, they also have some shortcomings. Here are some of them.
Expensive in Medical Settings
High-end lasers used in laser-based treatments and surgeries can be quite expensive. Their price may limit access to these procedures for some people.
Additionally, insurance companies may not cover the cost of laser treatments, deeming them \cosmetic procedures.
Injuries
Lasers can cause injuries, including burns and blindness. If not used properly, they can be very dangerous.
For example, if a laser is pointed at someone’s eyes, it can damage the retina. As a result, it can lead to partial or complete blindness.
Lasers can also cause fires if they come in contact with flammable materials. For instance, in laser welding, the laser’s intense heat can easily ignite metal shavings or dust.

Require Careful Handling
Laser welding, cladding, and cutting require great care and precision. The slightest mistake can result in imperfection or complete ruin of the material.
Even worse, these processes can be hazardous if the person operating the laser is not skilled. For example, laser cladding involves using a laser to apply a thin coating of material to another object. If not done correctly, the laser can overheat the material, causing it to catch fire.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is the Principle Behind Lasers?
A laser emits light through optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. In this process, the optical cavity produces a laser beam, which houses mirrors responsible for providing feedback. The electrons in the atoms are excited by an external energy source, such as an electrical current or flashlamp. When they return to a lower energy state, they emit photons in phase with each other. It creates a beam of coherent light.
What Is a Laser Beam Made Of?
A laser beam is made of photons, which are packets of energy. The photons are emitted from the atoms in the laser as they return to a lower energy state.
How Does a Laser Pen Work?
A laser pen has a battery-based power source. The laser beam is produced by a diode that is electrically stimulated. The light produced by the diode amplifies and passes through a series of mirrors. These mirrors create a beam of light focused on a small spot.
How Far Can a Laser Go?
It depends on the type of laser. Some lasers can travel long distances, while others are only meant for short-range use. Some lasers can go up to 10 miles of visible distance.
Why Is a Blue Laser More Powerful Than a Red Laser?
The blue laser has a shorter wavelength, which means it has more energy. In addition, the shorter wavelength allows the blue laser to be more focused than a red one.
What Are the Different Types of Lasers?
There are different lasers based on their wavelength, power, and mode of operation. The most common types are He-Ne, CO2, argon, krypton, and xenon lasers.

How Do I Choose the Right Laser for My Needs?
The type of laser you need depends on the application you are using it for. You also need to consider the power of the laser. The higher the power, the more expensive the laser will be.
How Does the Color of a Laser Affect Its Power?
The color of a laser does not affect its power. Instead, the wavelength of the light determines the power of the laser.
How Much Power Does a Laser Use?
It depends on the type of laser. Some lasers use more power than others. The power consumption of a laser is measured in watts.

Final Thoughts
Summing it up, lasers work by exciting atoms to produce photons. Different types of lasers create photons with different energies. Lasers are used in various applications, including cutting and welding, scanning, communications, and surgery.
The advantages of lasers include directional emission, monochromaticity, and high coherence. Lasers also emit extremely high levels of power. It makes them useful for numerous industrial and scientific applications.
Unfortunately, some of the dangers associated with lasers include eye damage, fires, and explosions. Therefore, it’s essential to be careful when using lasers and to follow safety precautions.
Featured Image Credit: nepool, Shutterstock
Table of Contents
- How Does It Work?
- What Are the Different Types of Lasers?
- Where Is It Used?
- Advantages of Lasers
- Disadvantages of Lasers
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What Is the Principle Behind Lasers?
- What Is a Laser Beam Made Of?
- How Does a Laser Pen Work?
- How Far Can a Laser Go?
- Why Is a Blue Laser More Powerful Than a Red Laser?
- What Are the Different Types of Lasers?
- How Do I Choose the Right Laser for My Needs?
- How Does the Color of a Laser Affect Its Power?
- How Much Power Does a Laser Use?
- Final Thoughts
About the Author Jeff Weishaupt
Jeff is a tech professional by day, writer, and amateur photographer by night. He's had the privilege of leading software teams for startups to the Fortune 100 over the past two decades. He currently works in the data privacy space. Jeff's amateur photography interests started in 2008 when he got his first DSLR camera, the Canon Rebel. Since then, he's taken tens of thousands of photos. His favorite handheld camera these days is his Google Pixel 6 XL. He loves taking photos of nature and his kids. In 2016, he bought his first drone, the Mavic Pro. Taking photos from the air is an amazing perspective, and he loves to take his drone while traveling.
Related Articles:
What Is the Best Binocular Magnification for Hunting? Optical Features Explained
How to Clean a Refractor Telescope: Step-by-Step Guide
How to Clean a Telescope Eyepiece: Step-by-Step Guide
How to Clean a Rifle Scope: 8 Expert Tips
Monocular vs Telescope: Differences Explained (With Pictures)
What Is a Monocular Used For? 8 Common Functions
How to Clean a Telescope Mirror: 8 Expert Tips
Brightfield vs Phase Contrast Microscopy: The Differences Explained
