What Is the Refractive Index of Air? Everything You Need to Know!
Last Updated on

The refractive index is a critical value that reveals a lot about a medium and how light interacts with it; it determines how much light is bent or refracted when it enters a material. The refractive index is a crucial factor in any optical instrument’s components. It allows the construction of lenses, which focus light to form real images.
The refractive index is represented by the ratio of two different speeds and is usually greater than 1. The refractive index of air is very similar to the refractive index of a vacuum, which helps calculate the refractive index of other media.

What Is Refraction?
Refraction is described as the bending of a light wave as it passes through two transparent mediums of different densities caused by the change in the wave’s speed.

What Is a Refractive Index?
The refractive index, also called the index of refraction, measures how quickly light rays travel through a given medium. It can also measure how a light ray bends when passing between mediums.
Because it can be represented as a ratio of two different speeds, the speed of light in a vacuum(c) and the speed of light(v) in a given medium, the index of refraction is a dimensionless quantity, usually represented by n=
The value of the refractive index is usually greater than or equal to one. The speed of light in a vacuum is always greater than the speed of light in any given medium. The higher a medium’s refractive index, the slower light travels through it.
The concept of refractive index is applicable not only in optics but also throughout the electromagnetic spectrum, from X-rays to radio waves. It can, in fact, be applied to waves such as sound waves.
Laws of Refraction
- The incident ray, reflected ray, and normal all lie in the same plane.
- The angle of incidence’s sine and the angle of refraction’s sine are constant.
Snell’s Law
Snell’s law in optics is a relationship between the path a ray of light takes when crossing the boundary of separation between two contacting substances and their respective refractive indices.
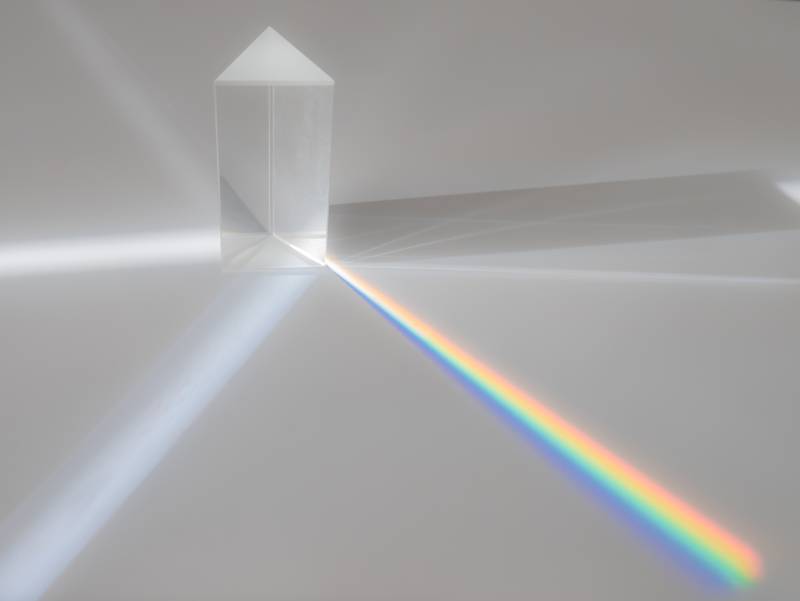

What Are the Different Types of Refractive Indexes?
The refractive index is of two types: the Absolute Refractive Index and the Relative Refractive Index.
The type of refractive index is determined by the two mediums through which the light travels. The relative refractive index describes the change in speed or velocity of light as it travels from one medium to another. The absolute refractive index has one material medium and one vacuum with a light speed of 3 × m/s.
When light rays travel from a rarer medium to a denser medium, they tend to bend towards the normal, whereas when they travel from denser to rarer, they bend away from the normal at the point of incidence. Its speed in air is also nearly identical to that in a vacuum, with only a minor difference. As the name implies, the absolute refractive index provides a rough estimate of the optical density of the given material.
What Is the Refractive Index of Air?
The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in air is defined as the index of refraction of air. The index of refraction for air is close to but greater than 1. The refraction index of air is 1.0003, which is very similar to the index of refraction in a vacuum (1.0000), so these indices are often used interchangeably.
The refraction index of air is a fixed number. However, there are minor variations in the value of the refractive index of air as certain quantities change.
- Lights wavelength: The refractive index of air varies with the wavelength. When white light travels through a prism, it disperses colors because light of different colors with different wavelengths has different refractive indices and therefore bends at different angles.
- Temperature: The index of refraction is usually calculated at room temperature and pressure, but the value of the refractive index can be affected by a significant change in temperature. As the temperature rises, the medium becomes less dense. The speed of light increases, and the refractive index decreases. When the temperature drops, the medium becomes denser. Therefore, the speed of light decreases. As a result, the refractive index rises.

How To Calculate the Refractive Index of Air
In a vacuum, the velocity of light is estimated to be 2.99792458 x m/s, and the experimentally determined velocity of light in air is 2.99704644 x m/s. In this case, light enters the Earth’s atmosphere from space to determine the refractive index of air. The first medium is space is a vacuum, and the second medium is air.
As a result, the refractive index of light in the air relative to the vacuum is approximately 1.0003. The refractive index of air is assumed to be “1” in most calculations where decimal points are not more significant.
Applications of the Refractive index of Air
- Determining the purity of air.
- Calculating the relative refractive index of other media such as glass, water, and metal because the refractive indexes of air and vacuum are nearly identical.
- Analyzing the concentration of toxic gasses in the air.
- Estimating the moisture content of the air.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is the refractive index of air greater than one?
The refractive index is always greater than one.
Is the refractive index of air dependent on temperature?
The refractive index is affected not only by the temperature but also by pressure, composition, and especially the wavelength of light.
Does light travel from glass to air?
Because glass is denser than air, a light ray passing through it slows down. If the beam comes into contact with the boundary at an angle to the normal, it bends towards the normal.

What is the refractive index of water?
Water’s refractive index is 1.333.
Which substance has the highest refractive index?
Diamond has the highest, with a value of 2.42.

Refraction Index Examples
The following table lists some of the most commonly used mediums with well-known refraction indices:
| Material | Refraction Index |
| Air | 1.0003 |
| Vacuum | 1.000 |
| Water | 1.333333 |
| Ice | 1.31 |
| Diamond | 2.417 |
| Glass | +- 1.5 |
| Ruby | 1.7 |

Summing Up
Refraction occurs when light travels between two transparent media of two different densities. As light travels through a medium, its speed changes depending on the nature of the medium. The Refractive index describes how much a light ray changes direction and its velocity when it travels from one medium to another.
The refraction index of air is influenced by temperature and wavelength. The index of refraction for air is close to but just greater than 1, which is very similar to a vacuum. The refraction index of air is 1.0003. Because the refractive index of air is close to that of a vacuum, it can be used to calculate the refractive index of other materials.
See also:
- What Is the Refractive Index of Glass? (Full Breakdown!)
- What Is the Refractive Index of Water? Everything You Need to Know!
Featured Image Credit: Andy119, Shutterstock
About the Author Robert Sparks
Robert’s obsession with all things optical started early in life, when his optician father would bring home prototypes for Robert to play with. Nowadays, Robert is dedicated to helping others find the right optics for their needs. His hobbies include astronomy, astrophysics, and model building. Originally from Newark, NJ, he resides in Santa Fe, New Mexico, where the nighttime skies are filled with glittering stars.
Related Articles:
What Is the Best Binocular Magnification for Hunting? Optical Features Explained
How to Clean a Refractor Telescope: Step-by-Step Guide
How to Clean a Telescope Eyepiece: Step-by-Step Guide
How to Clean a Rifle Scope: 8 Expert Tips
Monocular vs Telescope: Differences Explained (With Pictures)
What Is a Monocular Used For? 8 Common Functions
How to Clean a Telescope Mirror: 8 Expert Tips
Brightfield vs Phase Contrast Microscopy: The Differences Explained
