What Color Is Saturn? The Surprising Answer!
Last Updated on
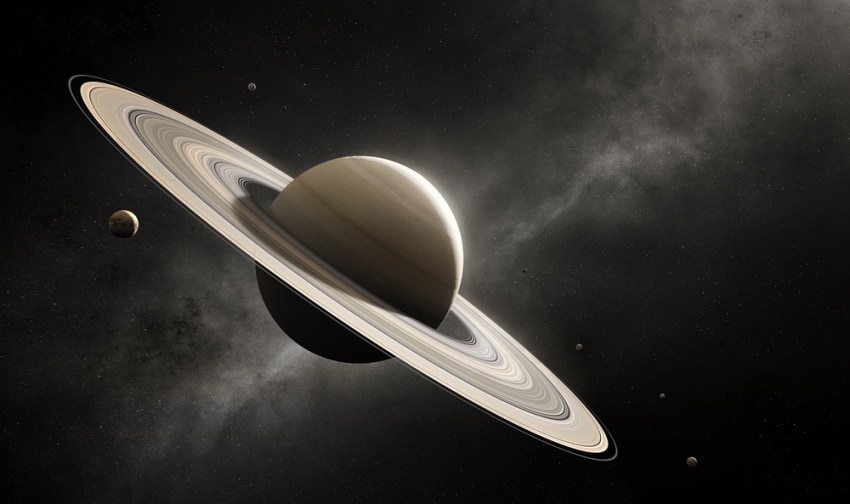

Saturn is the second-largest planet in the solar system, and it’s the sixth planet from the Sun. It’s one of the most unique planets due to its stunning colors and rings that make it stand out. Saturn’s rings have thousands of tiny ringlets composed of ice and rocks, giving it a unique appearance.
If you’ve ever looked up Saturn’s photos online, you’ll see various color schemes that could make you wonder what Saturn’s actual color is.
If that’s something that has crossed your mind, check out the rest of our article.

Why is Saturn Yellow and Brown?
Planets form their colors based on their materials and how their atmospheres or surfaces absorb sunlight. That’s why the Earth appears as a planet with blue, green, and brown colors, due to the water, forests, and land, while Mars is orange due to the iron oxide and dust particles.
In the same way, Saturn has specific colors because of the materials that form and surround the planet.
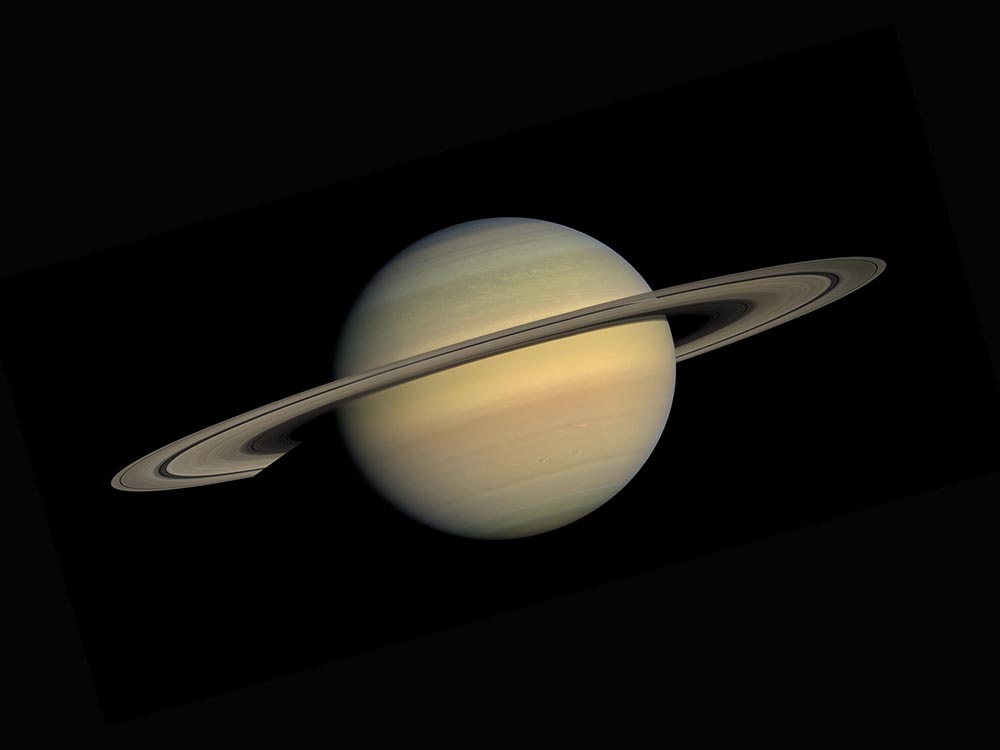
What’s Saturn made of?
When it comes to Saturn, it is made up of mostly helium and hydrogen, while its atmosphere has remnants of phosphine, ammonia, methane, hydrocarbons, and water vapor. That gives Saturn a hazy brownish-yellow color with hints of orange and gray.
When you observe Saturn through a telescope, you can see cloud layers with many different details inside, such as brown, white and red spots, eddies, vortices, and bands that switch on the surface.
The color we see is a mixture that occurs in the top and bottom cloud layers of Saturn, which contain ammonia crystals and wither water or ammonia hydrosulfide.
Can Saturn change colors?
Scientists have revealed that subtle changes are happening to Saturn’s color. The planet’s color slightly changes from season to season, and some parts of the planet become brighter while others get darker.
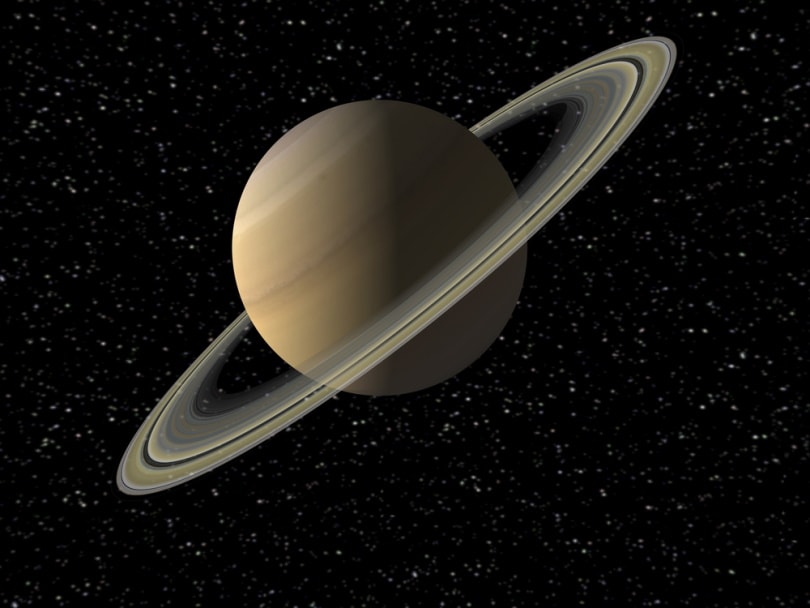

What Color are Saturn’s Rings?
Saturn contains seven stunning rings that also vary in color. They are mostly water and ice, and astronomers believe that their color will change depending on the contamination with other particles in the atmosphere.
They typically have sandy colors, with gray, brown, and pink hues.
What Colors are Saturn’s Moons?
Saturn has over 60 moons that can “change colors” depending on the brightness and particles that come in contact with them. The moons will appear brighter if the Sun is “overheated,” while the ones closest to the ring system will be slightly darker.
The moons get their color from a red material inside of Saturn’s rings or ice volcanoes, and their appearance will depend on their position compared to the rings. The closest moon to the rings will be the reddest, while the furthest moon will be the bluest.
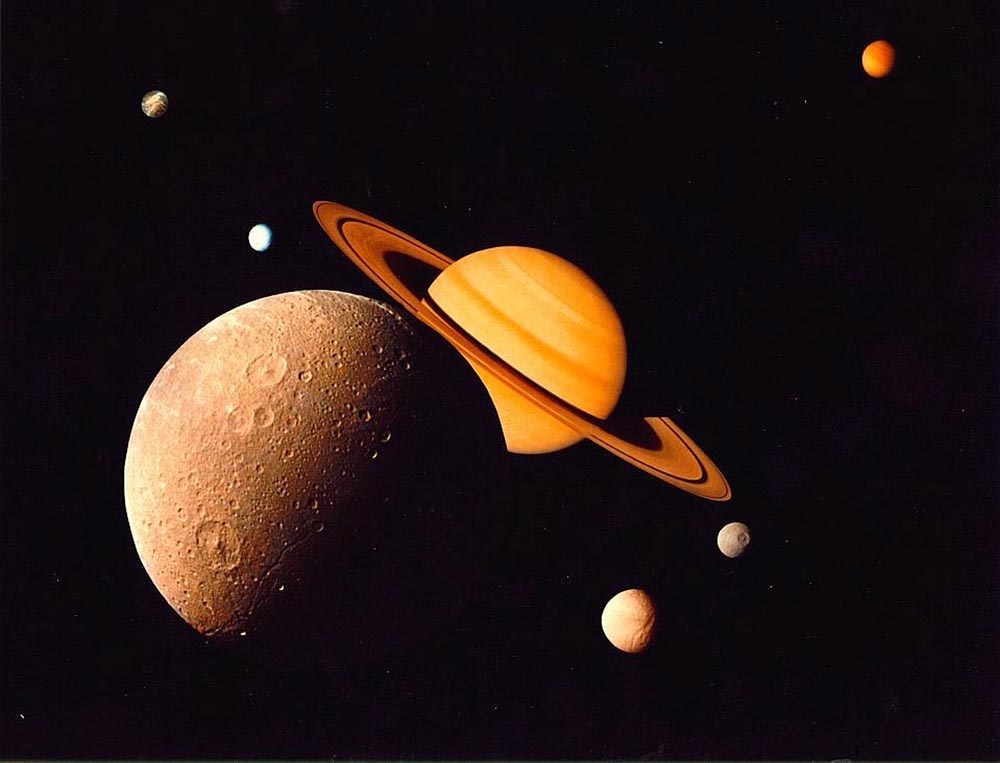

Some of the most famous of Saturn’s moons are:
| Prometheus | Bright shades |
| Pandora | Bright shades |
| Mimas | Darker shades |
| Tethys | Gray with reddish and orange hues |
| Rhea | Gray with reddish and orange hues |
| Dione | Gray |
| Hyperion | Very dark |

Conclusion
Saturn is truly a remarkable planet, and scientists are yet to find all the reasons why the planet changes colors and if the color will change with years or not. For now, the yellowish, brownish, and orange hues give it a hazy composition, while Saturn’s rings add flair and an exciting appearance to this unique planet.
Featured Image Credit: Johan Swanepoel, Shutterstock
About the Author Visnja Radosavljevic
Visnja is a creative, adaptable content writer that covers various topics such as DIY, pets, home improvement, travel, gardening, and more. As a young mom and a college student, she didn’t have enough time to balance her personal and work life, so after multiple years of working a regular 9 to 5 job, she decided to pursue her passion and make a living out of it. She has been writing for a couple of years now, helping people to find valuable and interesting information online.
Related Articles:
What Is the Best Binocular Magnification for Hunting? Optical Features Explained
How to Clean a Refractor Telescope: Step-by-Step Guide
How to Clean a Telescope Eyepiece: Step-by-Step Guide
How to Clean a Rifle Scope: 8 Expert Tips
Monocular vs Telescope: Differences Explained (With Pictures)
What Is a Monocular Used For? 8 Common Functions
How to Clean a Telescope Mirror: 8 Expert Tips
Brightfield vs Phase Contrast Microscopy: The Differences Explained
