Cormorant vs. Loon: How Are They Different?
Last Updated on
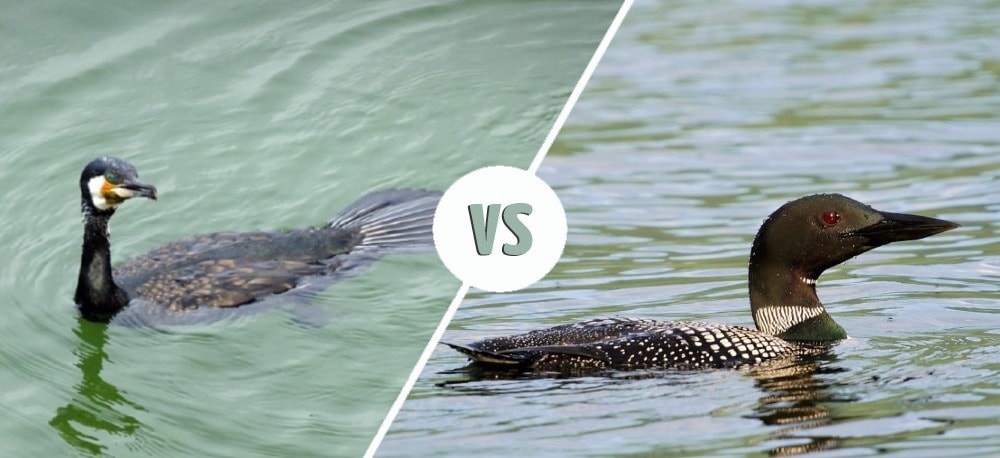
The lakes in the US and North America are home to numerous waterbirds that appear almost alike. Two of these birds are Cormorants and Loons, which look similar to geese from a distance.
Both are diving and fish lover birds closely related to each other. Appearance-wise, they both have heavy bodies that are partially submerged in water. However, they have a few differences in appearance and behavior, especially their calls.
Let’s explore how Cormorants and Loons differ to determine which is right for you.

Visual Differences

- Origin: French
- Size: 70–90 centimeters
- Lifespan: 11 years
- Domesticated?: No
- Origin: Scandinavian
- Size: 66–91 centimeters
- Lifespan: 30 years
- Domesticated?: No

Cormorant Overview
The Cormorant is a black waterfowl with a unique yellow-orange face. These bird species are closely related to boobies and frigatebirds, primarily found in saltwater and freshwater marshes across North America. However, these birds look like a mixture of Loons and geese.
Cormorants have solid, heavy bodies, making them experts at diving and catching small fish underwater. They gather the most attention when standing on rocky islands and spreading their wings.
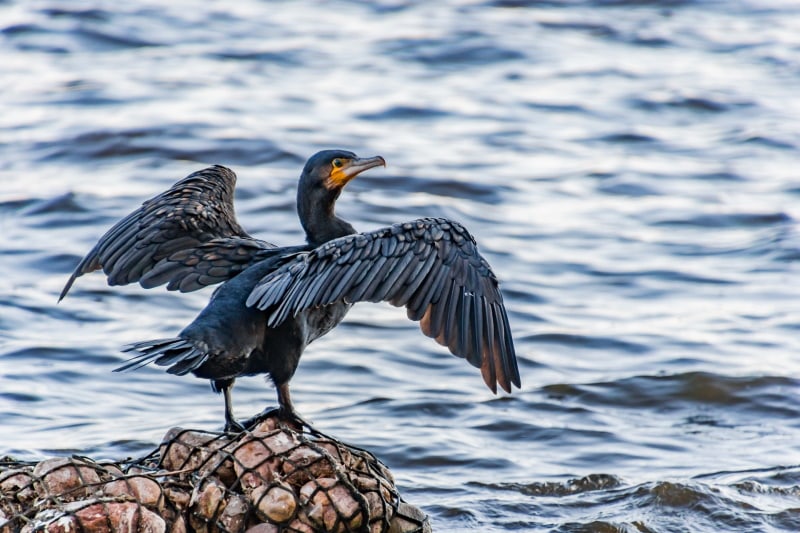

Their diet primarily consists of fish, which is why these birds are mostly found inhabiting near aquatic bodies. However, Cormorants may sometimes eat crustaceans, insects, or amphibians.
According to the International Ornithological Congress (IOC), 42 cormorant and shag species are present. A few include:
- Great Cormorant
- Double-crested Cormorant
- Pygmy Cormorant
- Reed Cormorant
- Crowned Cormorant
- Little Cormorant
- Red-legged Cormorant
Characteristics & Appearance
Cormorants are large matte-black birds with snake-like long necks and small heads. They have thin but powerful hooked bills, almost the size of their head. These birds have heavy bodies that allow them to sit low in water sources.
From the up-close, you’re more likely to be surprised by their gorgeous orange-yellow face and throat, sparkling aquamarine eyes, and bright blue area inside their mouths. These are the adult’s traits.
The average Cormorant is anywhere between a goose and a crow. Naturewise, Cormorants generally are non-aggressive birds but can display territorial behavior during the breeding season.
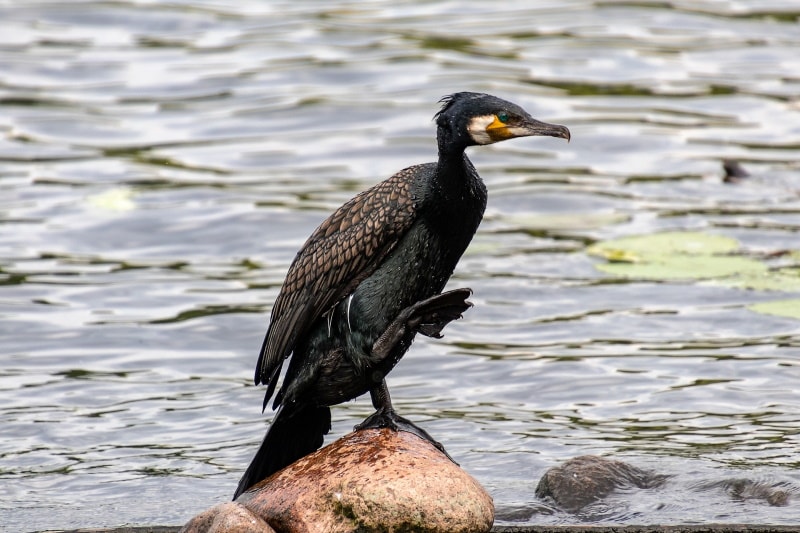

Uses
People have been using Cormorants for traditional human fishing for centuries. These birds are experts in catching fish, even from hard-to-reach areas. The Cormorant fishing method includes tying the bird’s neck to a net and setting it out in the sea to capture fish.
The primary purpose was to catch larger fishes, which usually get stuck around the Cormorant’s neck because of the net. However, they swallow smaller fish for their survival. Then, the Cormorant returns to the fishermen after catching multiple fish.
Cormorant fishing was quite popular in the olden days in Europe, including Greece, North Macedonia, and Asia. But it has become obsolete these days and is rarely seen in China.

Loon Overview
Loons are the iconic birds in the North Woods water habitats. Loons ensure water quality for many people since these birds only live in crystal-clear lakes with lots of small fish. They can easily spot their underwater prey in transparent water sources.
Loons are famous for their eerie calls that echo across the water habitats of the Northern areas. So, you’ll likely find these birds near shores and inland reservoirs during winters and summers. But unfortunately, they rarely come to the land.
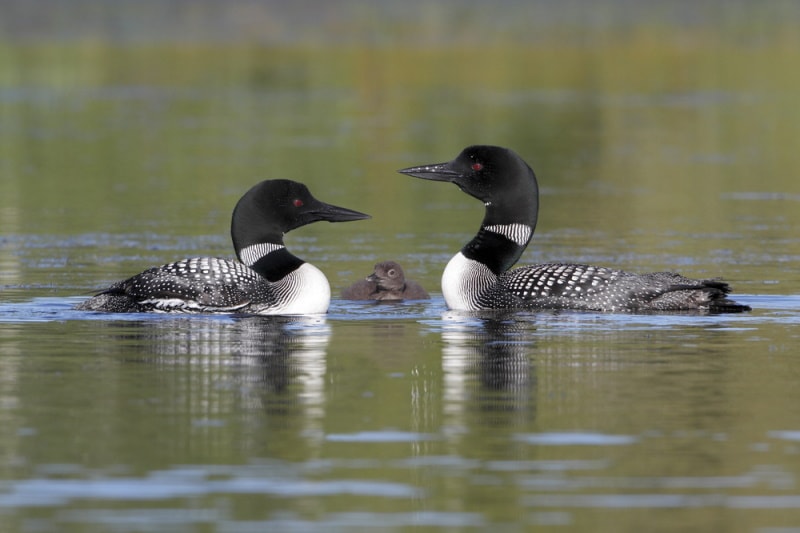

They are powerful underwater divers, capturing small fish in just a few dives. These birds have sharp pointy projections on their mouth and tongue roofs that strengthen their grip on fish.
Besides fish, Loons also feast on crustaceans, leeches, snails, and insect larvae. They are also quick flyers, as they can migrate at a speed of 70 miles per hour.
Currently, there are five officially-recognized Loon types present, including:
- Red-throated Loon
- Pacific Loon
- Common Loon
- Yellow-billed Loon
- Arctic Loon
Characteristics & Appearance
Common Loons are big, diving birds with bills similar to daggers. They have slender bodies with rounded heads and almost invisible tails.
When flying, these birds appear stretched with a long body, neck, and bill. Unlike Cormorants and ducks, their feet stick out from the tail, appearing as wedges. In summer, adult Loons have black bills and heads with black and white spots on the back and white chest.
Like Cormorants, the average size of a Loon is between a crow and a goose.
These birds are naturally non-aggressive but can be violent toward other Loons during the breeding season. They fight fiercely, sometimes causing fatal injuries to each other. Loons can also attack humans if they are provoked.
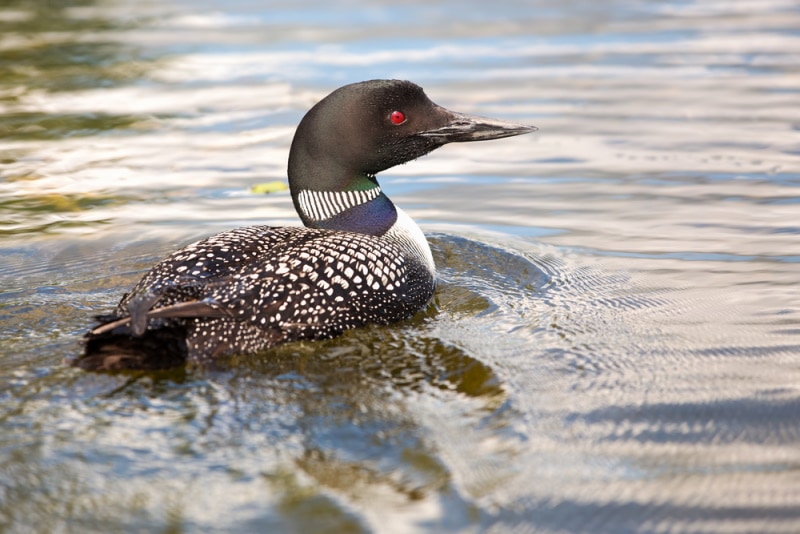

Uses
For years, Loons have been hunted by people and consumed fresh. In most cultures, such as Yukon, these birds are boiled or dried before eating, but their taste hasn’t been enjoyed much.
Besides food, Loons were used in Plains and Blackfoot cultures for medicinal bundles. For example, people filled the bird’s skin with hemp and grass. In Alaska, the bird’s skin was used to make coats and seats because of their warm and water-proof nature.
The Northwest Coast cultures made beds, hair accessories, and pillows from the Loon’s feathers. Their beaks made powerful arrowheads, while their wing feathers turned into brooms.
However, nowadays, these uses of Loons are not observed.
What Are the Differences Between Cormorants & Loons?
Many bird lovers and watchers confuse Cormorants and Loons because of their slender bodies. Not only that, but people use “geese” as a broader term to refer to both of these species.
Yes, Cormorants and Loons look pretty similar to geese, but they have significant differences in appearance. Here are a few:
- Body Appearance: Cormorants, especially Double-crested ones, have long, slender bodies with equally long necks. Meanwhile, Common Loons have heavier bodies with smaller and thicker necks.
- Bills: Cormorants have hooked yellow bills with an orangish patch on the base. On the other hand, the bills of Common Loons are black and pointed like that of a dagger.
- Behavior: Cormorants usually stand on docks and rocks with outstretched wings. Meanwhile, Loons can’t stand upright and only search for a dry habitat for nesting or safety.

Final Thoughts
Hopefully, now you can easily differentiate between Cormorants and Loons. Both are waterbirds and eat fish as their primary diet, but they have significant differences in appearance.
While Loons have heavier bodies and smaller necks, Cormorants have long bodies and necks. Remember that both species are not naturally aggressive but can get violent when provoked.
So, choose wisely and try not to disturb a busy Loon or Cormorant.
Featured Image Credit: (L) Piqsels | (R) Jody Parks, Pixabay
About the Author Jeff Weishaupt
Jeff is a tech professional by day, writer, and amateur photographer by night. He's had the privilege of leading software teams for startups to the Fortune 100 over the past two decades. He currently works in the data privacy space. Jeff's amateur photography interests started in 2008 when he got his first DSLR camera, the Canon Rebel. Since then, he's taken tens of thousands of photos. His favorite handheld camera these days is his Google Pixel 6 XL. He loves taking photos of nature and his kids. In 2016, he bought his first drone, the Mavic Pro. Taking photos from the air is an amazing perspective, and he loves to take his drone while traveling.
Related Articles:
10 Types of Hummingbirds in Arkansas (With Pictures)
8 Types of Hummingbirds in Nebraska (With Pictures)
5 Types of Hummingbirds in Idaho (With Pictures)
3 Types of Hummingbirds in Mississippi (With Pictures)
8 Types of Hummingbirds in Kansas (With Pictures)
5 Types of Hummingbirds in West Virginia (With Pictures)
5 Types of Hummingbirds in Ohio (With Pictures)
Where Do Nuthatches Nest? Nuthatch Nesting Habits Explained
